Microscopes and data analysis workstations
The core facility offers access to a variety of different microscopes that usually are prevalent in a particular scientific domain.
-
Multiphoton microscope
- Upright Bergamo II stand
- Epi-fluorescence: 5Mpix sCMOS
- Galvo scanner
- Resonant scanner
- Z-Piezzo (on objective)
- 2P Laser
- 3P Laser
-
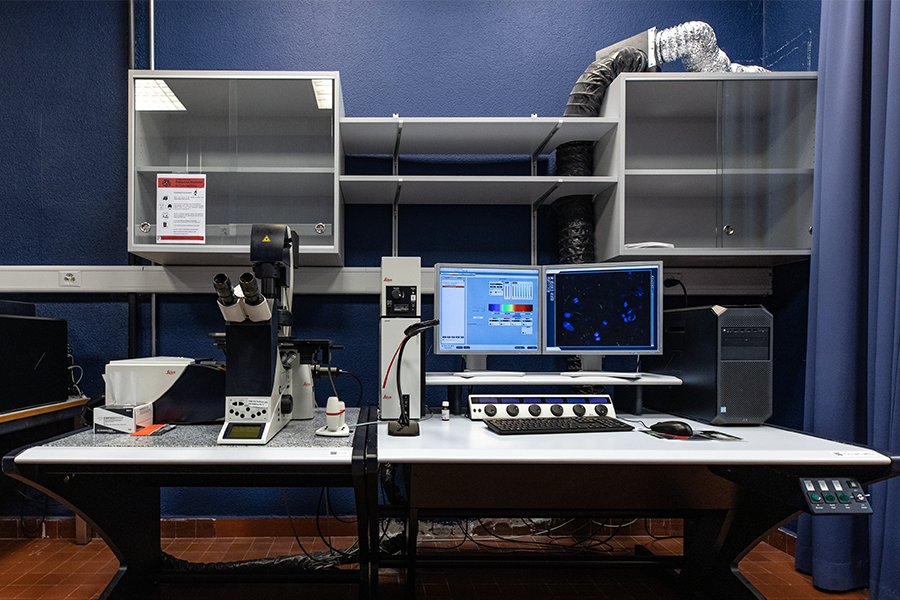
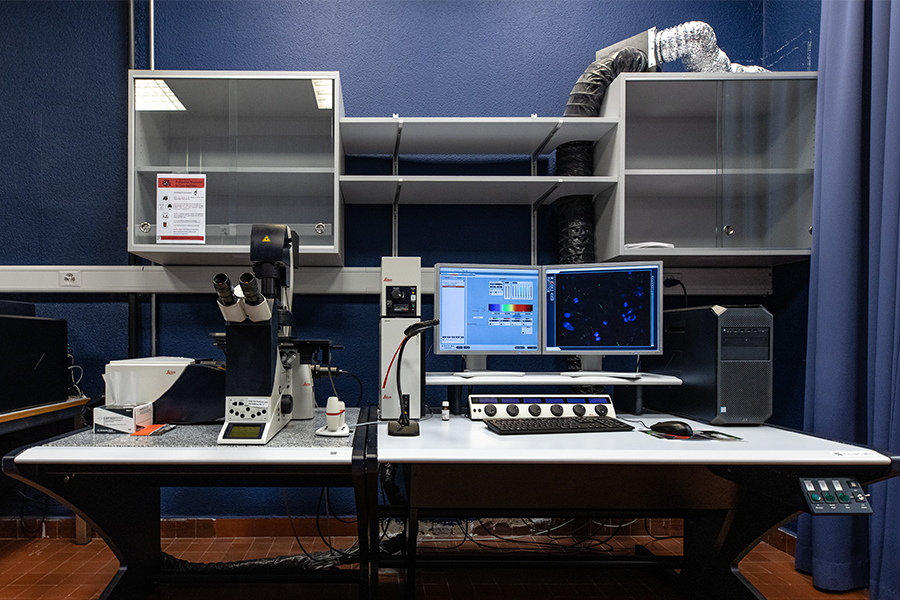
Laser scanning confocal
- Inverted DMi8 stand, fully motorized
- Diode laser: 405 nm
- Pulsed white light laser 440-790 nm (1nm steps)
- 4 HyD detectors (fluo)
- 1 PMT transmitted light
- Resonnant scanner 8kHz
- Environment control (T, CO2, humidity)
- Inverted DMI6000 stand, fully motorized
- 4 HyD and1 PMT detectors (fluo)
- 1 PMT transmitted light
- AOBS
- Galvo scanner 1-1400 Hz
- Resonnant scanner 8kHz
- Lasers line (nm)s: 405, 458, 476, 488, 496, 514, 561, 594, 633
- (Temperature controlled) plexiglas box
- Upright DM6000CS stand, fully motorized
- 3 PMT detectors (fluo)
- 1 PMT transmitted light
- AOBS
- Galvo scanner 1-1400 Hz
- Resonnant scanner 8kHz
- Laser lines (nm): 405, 458, 476, 488, 496, 514, 543, 633
- Upright DM5500Q
- Motorized stage
- 1 PMT (fluo)
- Lasers (nm): 405, 488, 532, 635
-
Spinning disk confocal
- Nikon Ti-E inverted microscope
- CSU-W1 Spinning Disk Head with 50um pinhole disk
- Evolve 512 (Photometrics) EM-CDD camera (16um pixel size)
- PCO.edge 4.2 sCMOS camera: (6.5 um)
- Environmental sample chamber (temperature and CO2 control)
- Photomanipulation module (FRAP, FRET, Photoactivation)
- Laser ablation module
-
Slide scanner
- Upright setup
- Wide-field color imaging
- Epi-fluorescence monochrome imaging
- 60/30 capacity of standard/double glass slides
- Upright setup
- Wide-field color imaging
- Epi-fluorescence monochrome imaging
- Capacity to load 210 standard glass slides
- Upright DM6B stand
- Fully motorized
- Large stage for multiple glass slides
- High speed sCMOS
- Color CMOS
- LAS X Navigator
- StereoInvestigator software
-
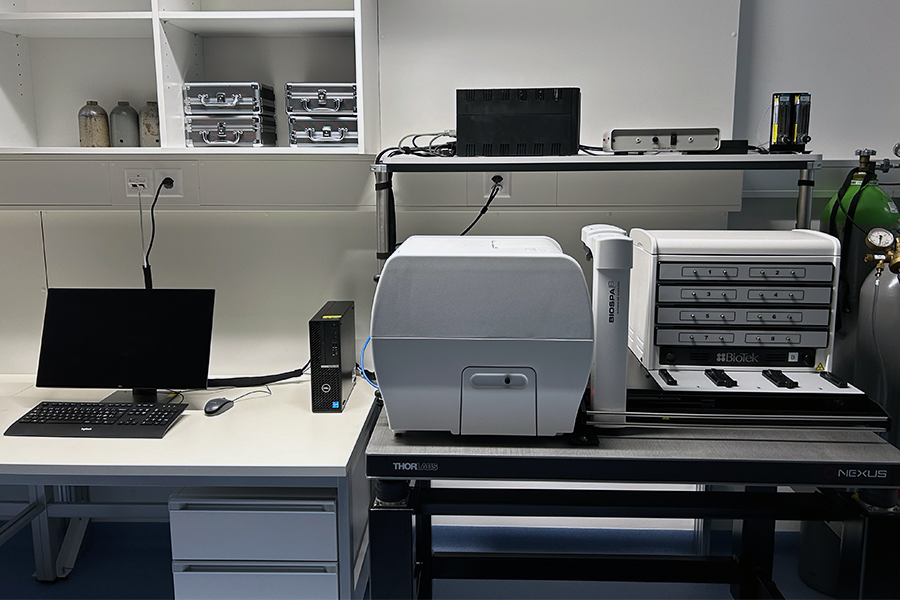
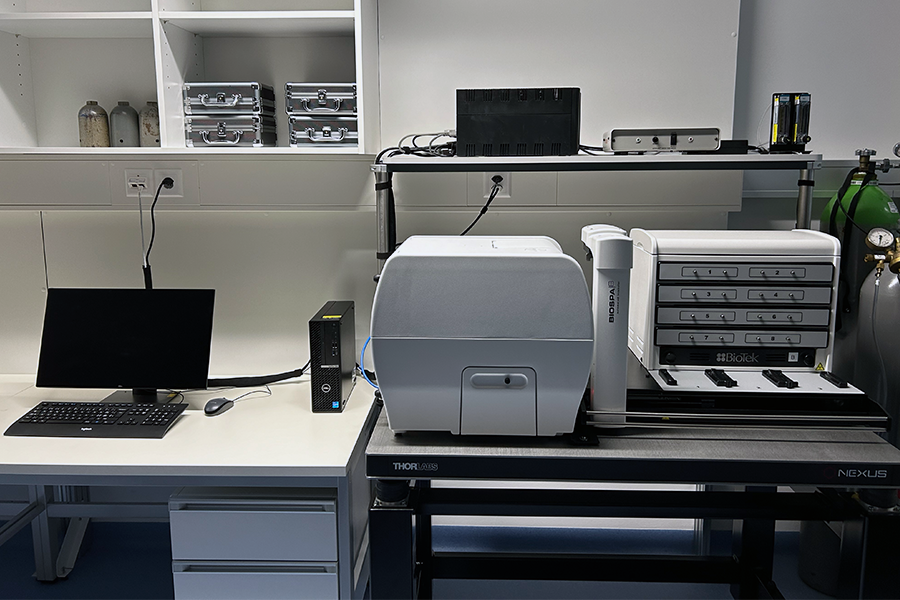
Live cell imaging microplate reader
- Imaging modalities:
- Bright-field
- Epi-fluorescence
- Absorbance
- Laser auto-focus module
- Incubator (termperature, CO2, humidity) with 8 slots
- 6-, 12-, 24-, 48-, 96-, 384- and 1536-well microplate compatible
(petri dishes, slides and flasks with adapters)
- Imaging modalities:
-
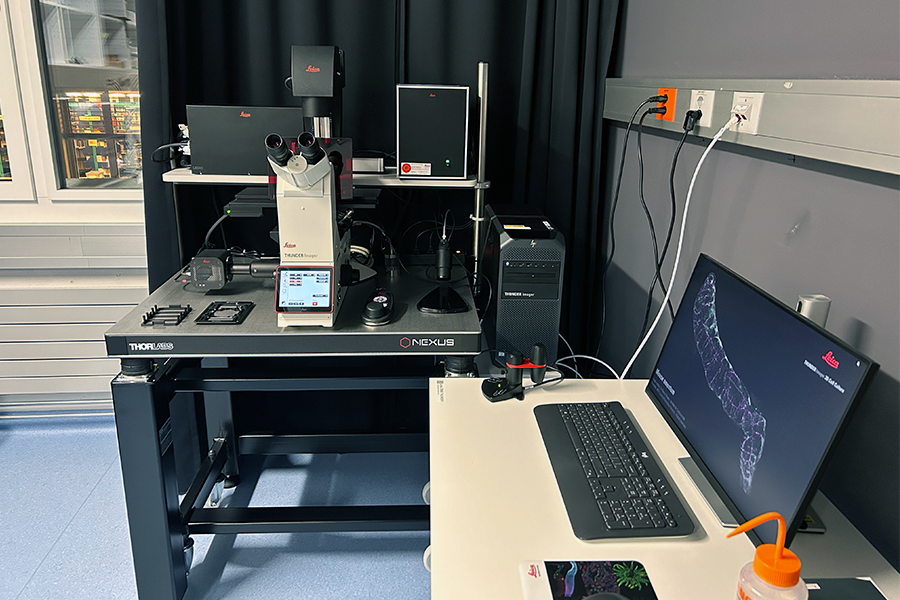
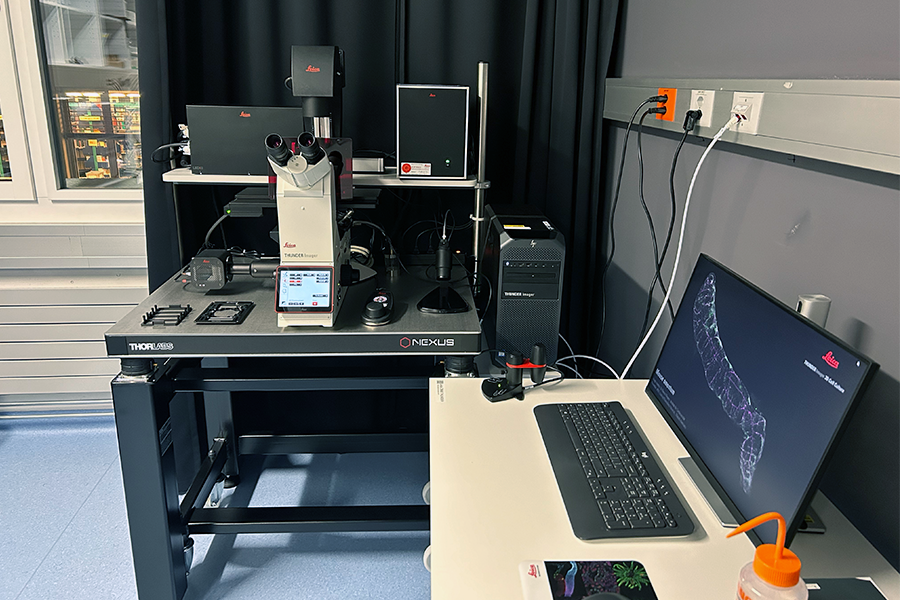
Wide-field microscope
- Inverted DMi8 stand, fully motorized
- Hardware autofocus
- K8 Camera (95 frames/sec, read noise 1.1 e- (RMS), max. QE 95%)
- Fluorescence light source : LED 8 (wavelengths)
- Fully automated, large ITK quantum stage
(mult-slide multi-well plate inserts) - Software modules: Navigator, deconvolution, computational clearing
- Inverted DMI6000 stand with motorized stage (only z-direction)
- DFC360FX CCD camera (1.4M pixels, 20 fps)
- Fast filter wheels (for FRET)
- FRET Wizard
-
Evanescent field microscope
- Oympus IX71 inverted stand
- CoolSnap HQ2 CCD camera
- Fast excitation/emission filter wheels
- Laser module for TIRF/FRAP
- Hardware autofocus
- Environment control (
C02, humidity and temperature) - Integrated deconvolution
-
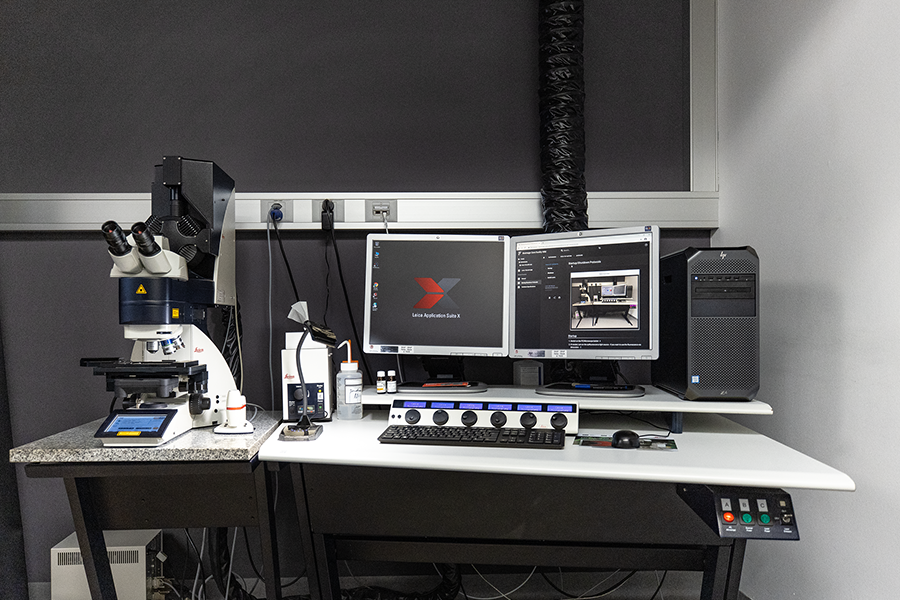
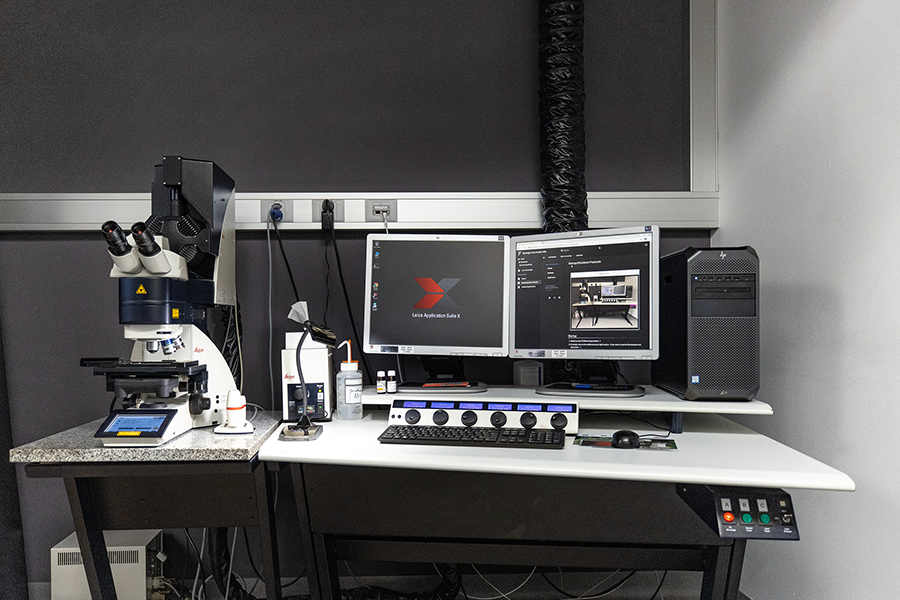
Data processing workstation
- Large 32'' screen
- High-end graphic card
- Fast network: ~800 MB/sec
- Large and Fast file storage (M.2 SSD)
- As much RAM as the motherboard can hold (64-128 GB)
Confocal systems can image an optical section through a translucent and fluorescently labeled sample. This can be used to get single high contrast images locations from relatively deep into the sample or for multiple consecutive sections for volume imaging. Confocal microscopes use either a point-wise scanner or a spinning disk, where the latter trades some of the capability to image deep into the sample for imaging speed.
Slide scanners focus on the throughput. Sample loading, scan area detection, determination of the focal plane and the scanning can be fully automated. The typical application cases are scanning of larger tissue sections, serial sections, and other types of sample collections.
Further (wide-field) applications include; a Stereology microscope allowing to quantify 1-3 dimensional structures by way of randomly sampling a set of sequential planar sections, a total internal reflection fluorescense (TIRF ) microscope to study small objects close to the cover glass at a high lateral resolution and a cell imager, to read out multiples measurements of single cells accros entire multiwell plates - also known as high content screening (HCS).
Most of the microscopes do not provide all software functionality to quantify the acquired data. For this reason, we also provide a number of image processing workstations, specifically tailored to the microscopy data.