Rates
-
SEM: 18.3 CHF/h

Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 2.21 Support 16.09 Training
115 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 4
-
Focused Ion Beam: 40.11 CHF/h

Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 16.33 Support 23.78 Training
700 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 10
-
Laser scanning Microscope: 13.68 CHF/h
Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 6.36 Support 7.32 Training
165 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 6
-
Darkfiels scattering microscope: Free of charge

Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 0 Support 0 Training
105 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 4
-
TEM: 27.92 CHF/h

Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 2.66 Support 25.26 Training
315 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 6
-
CryoTEM with sample preparation: 33.70 CHF/h

Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables
8.44 Support 25.26 Training
1546 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 14
-
Fluorescence Microscopy: 8.32 CHF/h

Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 6.36 Support 1.96 Training
135 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 4
-
Atomic Force Microscope: 1.29 CHF/h
Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 1.29 Support 0 Cantilevers are provided at 10 CHF/session Training
105 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 4
-
Small Angle X-ray Scattering:13.22 CHF/h
Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 3.36 Support 9.86 Training
105 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 8
-
Dynamic Light Scattering: 25.84 CHF/h

Rate (in CHF/h)
Consumables 1.01 Support 24.83 Training
105 CHF per user
Compexity Factor: 8
-
SNSF regulations
The hourly rates calculation are defined by the SNSF. Our costs only include the eligible costs.
1. Eligible costs
The eligible costs are the basis to calculate the hourly rate of an instrument for academic use. Practically, the hourly rate is based on scientific support and consumables.
Scientific support
The scientific support is all the support a user requires to measure his/her sample and get meaningful results for the project. It may support to the instrument, alignments of the instrument, support to design the experiments, sample preparation advice, help with the interpretation of the data or even performing experiments for the user. This support differs for every user, sample type, project and instrument. The concept to assign hourly rates to scientific support for microscopes is based on the observation that:
- Each user needs scientific support (e.g. for instrument calibrations).
- The amount of scientific support increases with the complexity of the instrument.
Since this differs from instrument to instrument, a Complexity Coefficient was introduced by the University of Zurich and has been accepted by the SNSF. The concept is also used in other UniFr facilities. Examples of the complexity coefficient for some instruments on the AMI booking platform:
Instrument Coefficient Atomic force microscope 4 Scanning electron microscope 4 Zeiss laser scanning microscope 4 Transmission electron microscope 6 Focused ion beam 8 These values are in accordance with other institutes, including the university of Zurich.
Consumables
Each purchase of consumable is logged to our consumables database. The costs of all consumables of an instrument is divided by the total hours the instrument is booked for scientific measurements. This yields the hourly consumables costs. Note: consumables bought by specific research groups (ie. not through the instrument specific account) are excluded from this calculation. The calculation integrates 3 years of consumables to avoid spikes in consumable costs.
Energy, chemicals, acquisitions and other eligible costs
These categories exists pro forma in the database, but are not included in the calculations.
- Energy is defined as the excess cost above normal energy use. This is not applicable for an instrument platform as AMI
- Chemicals are covered by the consumables
- Acquisitions: nothing additionally was acquired by an SNSF grant so far
- No other eligible costs were logged
2. Non-eligible costs
Non-eligible costs are not part of the hourly rate calculation for academic use.
Salaries of the maintenance personnel
Currently, no one is employed as maintenance personnel.
Maintenance contracts
Maintenance contracts were signed for most of the instruments and are covered by the Adolphe Merkle Institute.
Repairs
Repairs are covered by the Adolphe Merkle Institute (as far as they are not covered by the maintenance contracts), except repairs necessary due to gross misconduct by the user.In this case, the PI of the user is contacted and asked to cover the repair. See also the request for Introduction form.
Depreciation
The depreciation is a linear function of the initial purchase costs and the expected lifetime. For example, Laser scanning microscopes are considered a life span of about 10 years (also according to the international standard). With purchase costs of 500 000 CHF, a depreciation of 50 000 CHF per year is calculated. The hourly depreciation costs is the yearly depreciation cost divided by the total hours the instrument is booked for scientific measurements. It is excluded for academic use.
Other costs directly associated with infrastructure
Again the cost is spread over the years, as was the case for consumables and repairs. In this case, it is assumed that the acquisition or add-on will remain for the remaining lifetime of the instrument, unless clear otherwise.
Indirect costs
None of the indirect costs are currently considered. They cover the costs for e.g. the heating of the rooms, the rent of the building, the costs for chairs and lab equipment, the accounting personnel salaries etc.
-
Support
Scientific support
Scientific support is based on administrator attention (A), which is a function of
- the average number of active users (over the last 3 years)
- The complexity factor of the instrument
The more active users, and the complexer the instrument, the higher the attention of the admin to (the prjects) at a specific instrument.
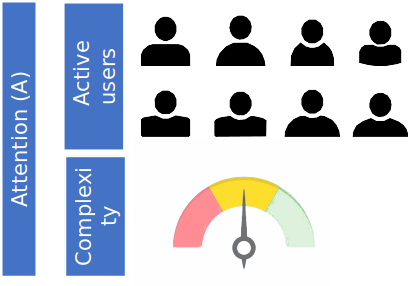
The attention is averaged over the booked hours (3 year average) and multiplied by the admin’s salary.
-
Consumables
Consumables
Consumables are entered in a database and the hourly costs for consumables is calculated by the total consumable costs (3 year average), divided by the total annually booked hours for that instrument (3-year average).
-
Trainings
Trainings
The cost for a training is calculated as cost of the session (duration x (hourly instrument cost + admin hourly cost)), divided by the average number of participants at a training.
